About signing algorithms
A digital signature is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient confidence that the message was created by a known sender and was not altered during transit. Digital signatures are commonly used when it is important to detect forgery or tampering.
About RSA algorithms
In RSA (Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman, the cryptosystem's inventors) cryptography, both the public and the private keys can encrypt a message; the opposite key from the one used to encrypt a message is used to decrypt it. This attribute is one reason why RSA has become the most widely used asymmetric algorithm: It provides a method of assuring the confidentiality, integrity, authenticity and non-reputability of electronic communications and data storage.
RSA derives its security from the difficulty of factoring large integers that are the product of two large prime numbers. Multiplying these two numbers is easy, but determining the original prime numbers from the total — factoring — is considered infeasible due to the time it would take even using today’s super computers.
BEST PRACTICE At a minimum, use SHA-256 encryption. SHA-1 has been known to be compromised.
-
Signing Algorithm Report
The Signing Algorithm report contains details related to Digital Signature Algorithms (signing algorithm) used by a Certificate Authority to sign a certificate.
-
CSR (Certificate Signing Request) Hash Algorithm
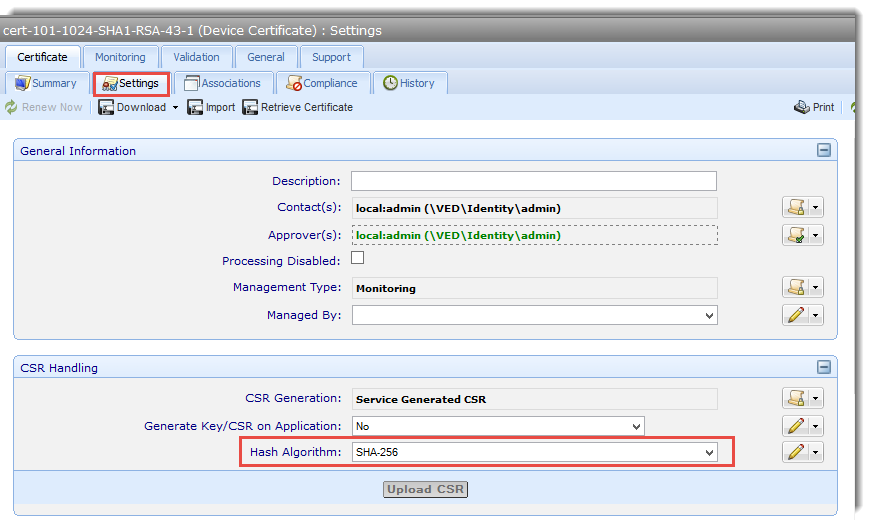 This is the hashing algorithm that is used to generate a hash of the data within the CSR. The result of that hash is then signed by the private key and added to the CSR. Thus, the CSR cannot be modified because the hashed data will have changed and the resulting hash will be different.
This is the hashing algorithm that is used to generate a hash of the data within the CSR. The result of that hash is then signed by the private key and added to the CSR. Thus, the CSR cannot be modified because the hashed data will have changed and the resulting hash will be different.