About RSA and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) key algorithms
RSA and ECC are two key algorithms. RSA is the most common; but ECC is gaining ground as an alternate, secure encryption method.
DID YOU KNOW? In RSA, the public key is a large number that is a product of two primes, plus a smaller number. The private key is a related number. In ECC, the public key is an equation for an elliptic curve and a point that lies on that curve. The private key is a number.
When you're deciding which algorithm to use for encryption, consider the following points:
- While in several respects, ECC is considered a viable option, some devices don't yet support ECC
- Trust Protection Foundation supports the 3 primary NIST-supported ECC key strengths, and only supports NIST EC curves. For example, we do support PRIME256v1. We do not support SECP256k1.
- Both the Apache and CAPI drivers support ECC
NOTE ECC support using the Apache driver applies to SafeNet Luna SA only.
Comparing RSA and ECC key algorithms
- RSA is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm used to encrypt and decrypt messages using public and private keys.
-
ECC is an algorithmic alternative to RSA that can have computational benefits because its size is smaller but comparably stronger. ECC-enabled TLS can be faster and more scalable and provides the same or better security than the default cryptography that is currently in general use.
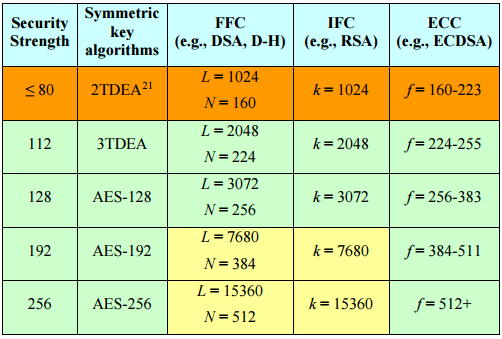
Courtesy of E. Barker, "Recommendation for Key Management -- Part 1: General (Revision 4),'' NIST Special Publication, SP 800-57R4, 2016-01, National Institute of Standards and Technology