Overview of certificate types
In addition to the traditional SSL/TLS (server) certificate, Trust Protection Foundation recognizes User certificates, Client Device certificates, and Code Signing certificates.
Each certificate type has its own icon.
BEST PRACTICE Certificate types are important because they let you organize and view your entire certificate population, by type. With four types of certificates, Trust Protection Foundation is able to be more selective with new or existing features like validation and provisioning.
When an employee is reassigned or leaves the company, knowing the number and types of certificates they managed or owned is critical.
Finally, running a report that shows you the number of each type of certificate being used by your company helps ensure that your company is in compliance with Trust Protection Foundation's licensing requirements.
SSL certificates are data files that digitally bind a cryptographic key to an organization’s details. Typically, SSL is used to secure, among other things, data transfer and logins.
SSL certificates bind together:
- A domain name, server name, or hostname
- An organizational identity (i.e. company name) and location
In Trust Protection Foundation, a certificate is classified as a SSL/TLS if it has an extended key usage (EKU) of Server Authentication.
A code signing certificate is used to digitally sign software programs as a way for software recipients to verify the authenticity and integrity of the software.
In Trust Protection Foundation, a certificate is classified as a code signing certificate if it contains and extended key usage (EKU) of Code Signing.
In Trust Protection Foundation, a certificate is classified as a user certificate if it meets the following criteria:
- Does not have an extended key usage (EKU) of Server Authentication or Code Signing
- Is a Smart Card
- SAN Principal = UPN, email, or RFC822
- Subject Type = User
In Trust Protection Foundation, a certificate is classified as a client device certificate if does not meet any of the criteria specified for the previous certificate types.
In Trust Protection Foundation, a time stamping certificate provides RFC 3161-compliant time stamping for code signing. It is used as part of the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted product. For more information about time stamping, see Understanding time stamping in code signing and Using the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted Time Stamp Service.
NOTE The CA/Browser forum has special rules around time stamping certificates. While such a certificate is issued with long (5 or more years) validity, the rules require that the certificate be re-keyed every 15 months. Trust Protection Foundation enforces this rule, both for notifications as well as for renewal. This means that a time stamping certificate that is 15 months old will be automatically renewed if set to enrollment. The notifications will be sent according to regular configuration settings, except that they will consider the cert issuance date + 15 months as the expiration. To avoid confusion, notification events for time stamping certificates explain this.
CA/Browser forum rules also require that the key of a time stamping certificate be stored in hardware only. Trust Protection Foundation will issue an alert-level notification if the certificate key is stored in software. The Time Stamping settings tab in Policy Tree provides a dropdown allowing you to select where they key should be stored.
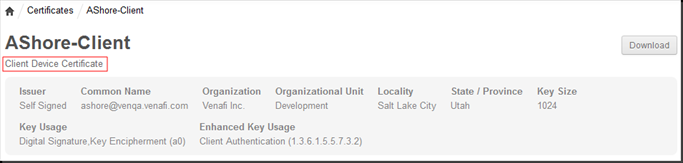
A certificate type displayed in Certificate Manager - Self-Hosted:
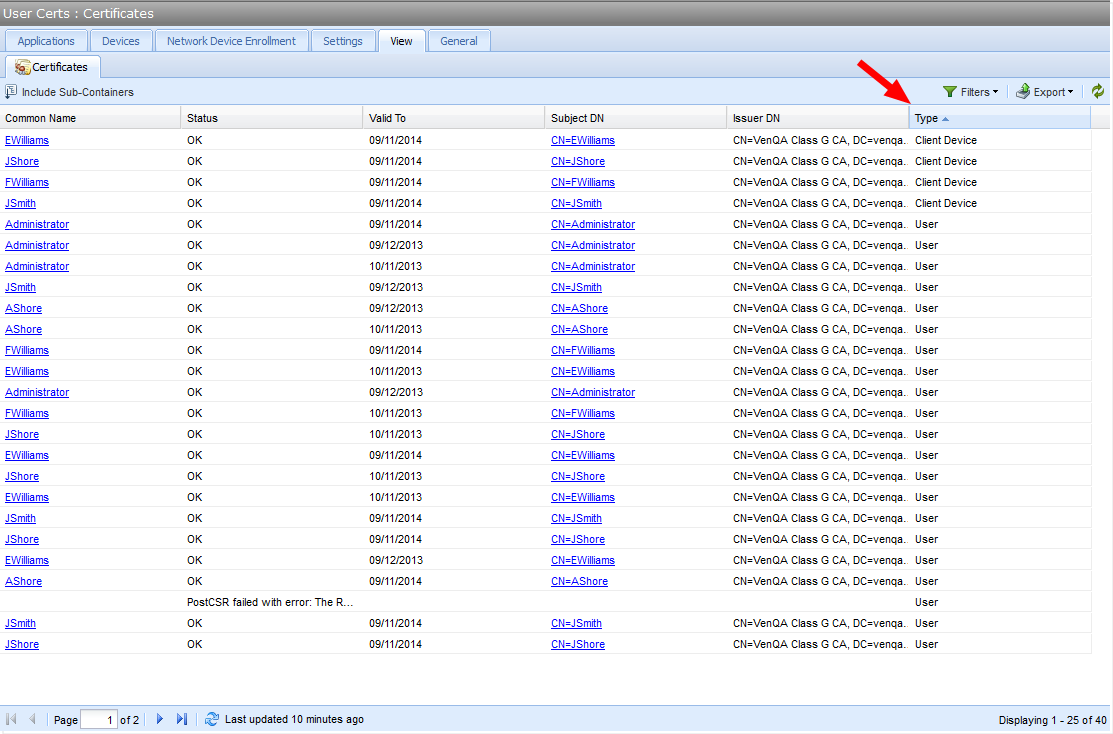
You can see the types of all certificates under a policy.
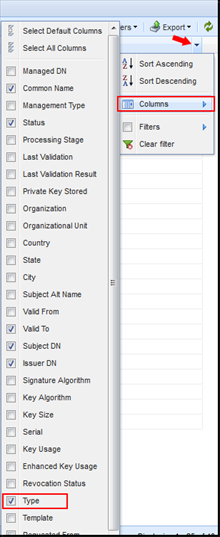
- In the Policy tree, select the policy containing the certificates you want to see.
-
Click the View tab.
You'll see a grid view of the certificates governed by that policy, and their attributes.
-
Click the drop-down arrow, select Columns, then select Type.