Certificate enrollment via SCEP protocol
As part of Trust Protection Foundation, the VEDSCEP application server manages certificate signing requests (CSR) and renewals for Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) certificates. SCEP certificates protect network mobile devices that are SCEP-enabled.
An external SCEP client, such as a network device or testing tool like SSCEP, can perform the following functions:
-
Initiate a certificate enrollment.
The VEDSCEP server accepts a PKCS #10 certificate signing request (CSR).
-
Request a certificate renewal.
The renewal requests are signed by prior (expiring) certificate.
- Retrieve a CA and RA certificate from the VEDSCEP server.
For example, a SCEP client initiates enrollment requests to the VEDSCEP server. VEDSCEP creates certificate objects in Trust Protection Foundation and marks them to be worked on by the system. The VEDSCEP server acts as an intermediary registration authority (RA) to the CA that signs certificates. The signed and encrypted format is PKCS #7.
Trust Protection Foundation manages requests based on one or more CA templates. The CA must support CSR requests that do not need prior authorization.
For example, Trust Protection Foundation can enroll both standard and EV SSL certificates with the Symantec MPKI CA. Additional NDE settings manage enrollment, certificate retrieval, and provisioning to the SCEP device.
Enrolling Standard and EV SSL Certificates with Symantec MPKI CA
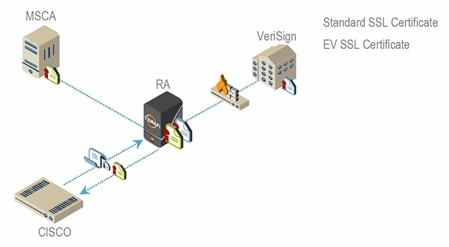
When initiating a request, the SCEP client must provide the correct VEDSCEP URL. If only one CA services SCEP enrollments, the URL is http://VED_server_address/vedscep/. For multiple CAs and CA templates, the SCEP client sends the base URL plus a CA identification string. The CA identifier is available from the Policy Tree CA template.
When the VEDSCEP receives an initial GET CA request from a network device, it returns the corresponding CA root certificate chain and its own RA certificate. The RA certificate is a Trust Protection Foundation signing certificate for the enrollment CA. In practice, the RA certificate can be a standard Web certificate. The only requirement is that the certificate must be signed by the enrollment CA. If you are managing certificate enrollment with multiple CAs, you must have a separate RA certificate for each CA. The RA certificate is used as a credential to validate the identity of the RA server. Both the SCEP device and the enrollment CA require the RA certificate before they can trust the Trust Protection Foundation server as the intermediary agent in the certificate enrollment process.
When Trust Protection Foundation receives the subsequent enrollment request, it first creates the Certificate object in the Policy tree, then submits the CSR to the appropriate CA for enrollment. After the CA signs the certificate, Trust Protection Foundation retrieves the certificate from the CA, then returns the certificate to the SCEP device.
TIP To browse topics in this section, use the menu on the left side of this page.