Managing Local Certificates Via Policy
Policies allow administrators to define global configuration parameters, or “folders,” for encryption resources associated with that policy, including local Certificate objects. For example, within a policy, you can standardize the key strength for all certificates created in that policy.
When a system object is defined under a policy object in the Policy Tree, the object and its corresponding resource are associated with the policy and are subject to the policy settings.
EXAMPLE If you configured the certificate management type in a Policy object, Trust Protection Foundation would read those values for the policy’s subordinate Certificate objects. Thus, policies can be used to standardize object configuration parameters and enforce security requirements.
For more detailed information on how folders work, see Using policies to manage encryption assets.
You must have View and Write permissions on the object for which you want to configure settings.
- From the Certificate Manager - Self-Hosted menu bar, click Policy Tree
-
In the Policy tree, select the Policy object where you want to configure certificate settings, and then click the Settings tab.
The Detail View displays the Policy object’s associated settings.
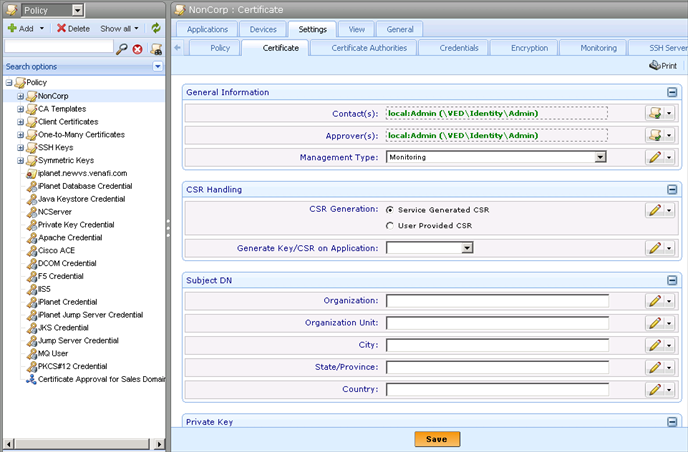
There are two Policy configurations for Certificate objects: the Certificate and Monitoring tabs. The following sections outline these configuration options:
- Define the settings you want to apply to the policy’s subordinate Certificate objects.
-
Lock or unlock the value.
When you define an attribute within a Policy object, you can lock or unlock the value.Locked attributes cannot be modified in objects contained by that policy, including sub-policies. Unlocked attributes function as suggested values; they can be accepted or overwritten in the subordinate object configuration.
By default, policy values are unlocked
 .
.
-
Click the Unlocked icon
 .
. The value toggles between a locked
 and unlocked
and unlocked  state.
state. - When finished, click Save/Apply.