Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted architecture
The Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted solution consists of the following components:
- Trust Protection Foundation server with Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted enabled. Throughout this article, this is referred to as the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server.
- CyberArk Code Signing clients, installed on the Windows, Linux, or macOS workstations from which code will be signed
- Optionally, a Hardware Security Module (HSM) connected to the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server to generate and store private code signing keys
All code signing private keys are stored in either the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted Secret Store or in an attached HSM.
CyberArk Code Sign Clients
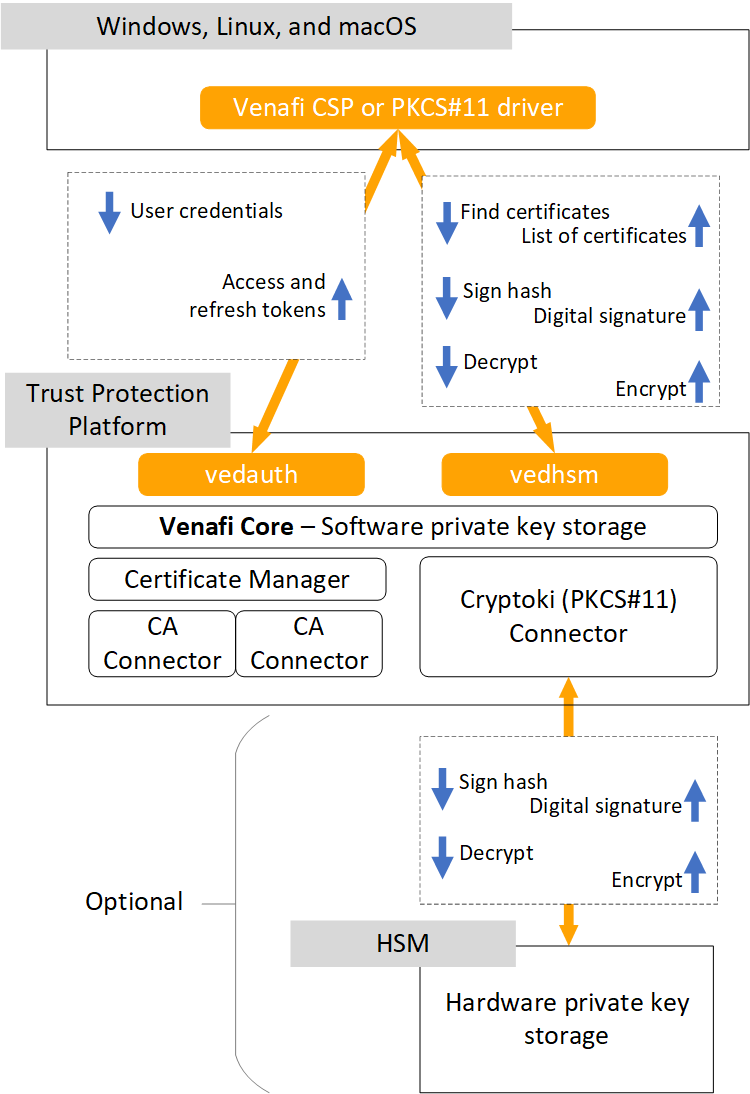
The Code Sign Clients link code signing workstations to the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server, which stores and manages use of private code signing keys. The Code Sign Clients communicate with the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server over a TLS-encrypted REST API. The following code signing clients are available:
- Windows: CSP/KSP, PKCS#11, and GPG clients
- Linux: PKCS#11 and GPG clients
- macOS: PKCS#11, Keychain Access, and GPG clients
During Code Signing Client configuration, you will provide the address of the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server you want to connect to and whether you want an access grant for the current user, local machine, or both. These options are described in the next section.
For more information on installing the Code Signing Clients, see Install Code Sign Clients on signing workstations. For more information about using the clients, see the sections for PKCS#11, CSP, GPG, and Keychain Access.
Trust Protection Foundation server
The Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server is the central orchestrator of the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted solution, and its job is to protect and govern the use of private code signing keys. All the keys are stored in either the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted Secret Store or on an HSM. The Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server performs the following functions:
- Authenticates users
- Issues certificate signing requests for approved code signing projects
- Stores code signing certificates
- Stores and protects private code signing keys
- Receives code signing requests
- Enforces permitted uses of private code signing keys
- Manages code signing request flows
- Returns signed hash to the requesting workstation
IMPORTANT The role of CyberArk Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted is to protect private code signing keys and to govern the use of those keys. CyberArk Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted itself does not sign code.
To facilitate authentication and virtual HSM functions, Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted uses these two endpoints:
Hardware Security Module (HSM)
As an optional feature, Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted can sign code with keys that are generated and reside on a Hardware Security Module (HSM). When the private key is on the HSM, a reference to that key is stored in the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted Secret Store. When a request is made to sign a hash with that key, Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted forwards the request to the HSM. The signing occurs on the HSM, which then returns the signed hash to the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server. In turn, the Code Sign Manager - Self-Hosted server returns the signed hash to the CSP.
Using an HSM for code signing requires the use of a supported HSM and activation of Advanced Key Protect, which is a separately-licensed component.
For more information about HSM integration with Trust Protection Foundation, see Managing system encryption keys.