Recycle Bin's actions panel
The Actions panel has the following options. When reviewing the following note the difference between deletion tasks and the purging of data. A deletion task can find old data in Secret Store and automatically move it to the recycle bin. Purging data is the process of permanently "emptying" the recycle bin.
-
 Configuration...
Configuration...
Purge items deleted more than ... - Changes the settings for how the purge action works. You can determine the length of time items in the recycle bin can remain before they are purged.
Limit purge process runtime... - You can limit the amount of time a purge process can run (to minimize impact on other resources).
Engine to run... - You can select which CyberArk Trust Protection Foundation - Self-Hosted engine performs the purge tasks, which also allows you to minimize impact on other server processes.
The default settings are to purge deleted items more than 14 days old, to limit process runtime to 3 hours, and to use any available engine. If you modify these settings, the entries list in the recycle bin immediately updates to show the new automatic purge date1.
The purge process runs with other daily tasks that run on the server. By default, the server runs daily tasks at midnight. You can modify this in engine's settings on the engine settings.2
If there are more items to purge than the limit imposed by the above settings, the purge process will continue during the next task window. The process will continue until all items have been purged from the system.
As a system administrator you may want to routinely monitor the recycle bin's logs in the Event Viewer to ensure old data is being purged at an appropriate rate. If you aren't purging a sufficient number of items, you can increase the runtime.
If you have been using Trust Protection Foundation for a long time, or if you have a lot of old data in your system, this process may initially take several days (or even weeks) to complete. After the initial purge has completed, you should adjust your settings to ensure enough items can be purged each day.
The process was designed to minimize impact to system resources, but if you find that deletions aren't happening as quickly as you expected, or if you notice an impact on performance, you might try setting up a new engine specifically for deleting and purging.
-
 Deletion Tasks...
Deletion Tasks...
To minimize storage space and to comply with industry or organizational policies, CyberArk Trust Protection Foundation - Self-Hosted can regularly clean up old data that may no longer be useful. We call this cleanup process "Deletion Tasks." The Deletion Tasks... action lets you customize your cleanup settings.
To customize settings related to performance, you can adjust the following settings:
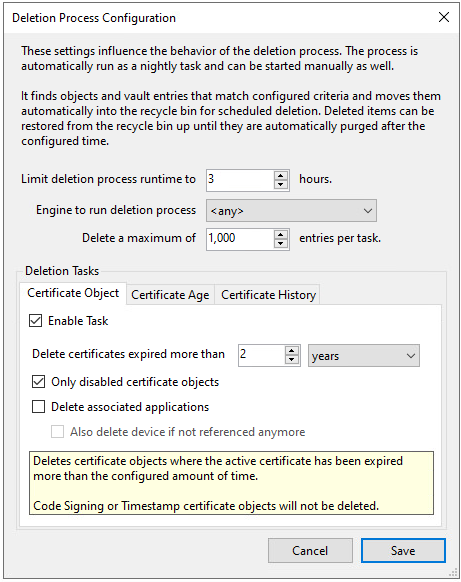
- Limit deletion process runtime. Configure the length of time the recycle bin can spend working on an automatic deletion action. The default is 3 hours.
-
Engine to run deletion process. Specify which engine performs the deletion tasks.
TIP If you need improved performance, consider creating an engine specifically for deleting and purging.
- Delete a maximum... Choose how many entries are deleted in a given task. The default is 1000 entries.
When the system reaches either the time limit or the number of entries limit, it pauses processing deletion tasks, and waits for the engine's next task window to continue. The process will continue until all items have been deleted and moved to the recycle bin.
As a system administrator, you may want to routinely monitor the recycle bin's logs in the Event Viewer to ensure old data is being moved to the recycle bin at an appropriate rate.
If you have been using Trust Protection Foundation for a long time, or if you have a lot of old data in your system, this process may initially take several days (or even weeks) to complete. After the initial deletion tasks have completed, you should adjust your settings to ensure enough items can be automatically deleted each day.
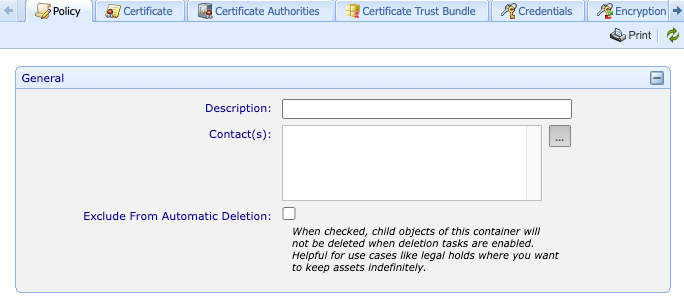
NOTE There is a configuration that exists on all WebAdmin policy objects called Exclude from automatic deletion. When this setting is enabled, these objects will be ignored by the automatic deletion features of the Recycle Bin. A use case for this feature is when there is a legal hold where you want to maintain assets indefinitely.
From the menu, click Policy Tree, then click on a policy object (not on a certificate object). Look at the Settings tab, Policy sub-tab. In the General section, you can click Exclude From Automatic Deletion.
Determine which deletion tasks are run (Deletion Tasks tabs).
You can automatically clean up X.509 certificates (not SSH certificates or code signing certificates) based on the following system parameters. If you would like to have certificate objects cleaned up then please enable and configure the Certificate Objects deletion task.
The Certificate Age and Certificate History deletion tasks are configured to operate exclusively on archived certificates. This ensures that only those certificates specifically designated for deletion are processed.
Each type of deletion task has its own tab on the Delete Process Configuration screen.
-
Certificate Object: Considers details about the certificate object's active certificate to determine if the certificate object should be deleted. The settings are:
-
Enable or disable this deletion task.
-
Specify the time period to use for deletion. Certificate objects that expired longer ago than the specified time would be considered for deletion, based on the other settings on this tab.
-
Choose if you want to delete all certificates, including old active certificates, or if you only want to delete disabled certificate objects.
-
Choose if you also want to delete associated applications.
-
If you do delete the applications that used this certificate object, you can also delete any unreferenced devices. This can help maintain an accurate list of devices by helping prevent orphaned device objects.
-
- Certificate age: Deletes certificate data for all certificates3 that are older than a specified number of years4. The settings are:
- Enable or disable this deletion task.
- Specify the time period to use for deletion. Certificates older than this age will be deleted and moved to the recycle bin.
- Specify whether active certificates can be deleted, or if only archived certificates (but not the most recent archived certificate) are deleted. When this option is selected, only archived certificate data (older than the most recent certificate) will be deleted.
- Certificate history: Determines the number of versions of a certificate are retained. This allows you to maintain, for example, the Secret Store data from the five most recent versions of a certificate, but if seven historical certificates are found, it will delete the Secret Store data of the oldest two, so five versions would remain in history. The settings are:
- Enable or disable this deletion task.
- Specify the number of versions of a certificate to retain.
-
Purge all... or Purge all in background...
Performs an immediate, irreversible purge of all items in the recycle bin. By default, a confirmation modal appears, which can be disabled.
The label depends on the amount of data in the recycle bin. If the amount of data to purge is small, you see Purge all... and the system purges the data while you wait. If the amount of data would take a longer time to purge, you see Purge all in background... which starts the purge as a background task so you can continue using the snap-in or console. If you click Refresh in the console, the refreshed contents will allow you to see how far the purge has progressed.
-
An MMC standard action that lets you customize the view of the overall console and which has not been modified by CyberArk.
-
Perform an immediate refresh of the contents of the recycle bin. As you take actions on the recycle bin, it automatically refreshes. This option allows you to refresh without taking any other action.
What's next
If you want to take action on a single recycle bin entry, see Recycle Bin's details panel.
If you want to see the recycle bin events in the Events Viewer, see Events overview
For information about the recycle bin main panel interface, see Recycle Bin's interface.